Unveiling the Hidden Impact of E-Waste
Did you know that E-waste is the fastest-growing waste stream globally. With rapid technological advances, more devices are being discarded each year. In this post, we will talk about how E-waste is harmful and ways you can make a difference in the reduction of E-waste.

- Impact Hub Nairobi
- Grace M
The Growing Crisis of Electronic Waste
As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented rate, the lifespan of electronic devices is becoming increasingly shorter. This has led to a mounting crisis of electronic waste, or e-waste, which refers to discarded electronic appliances such as mobile phones, computers, and televisions. The accumulation of e-waste has become a global concern with significant environmental, health, and economic implications. Millions of tons of e-waste are generated annually, with only a fraction being properly recycled, leading to vast amounts of hazardous materials entering landfills and the environment.
The situation is exacerbated by the rapid growth in the production of electronic goods, driven by consumer demand for the latest gadgets and the frequent release of new models. Without adequate recycling infrastructure and public awareness, the e-waste crisis is poised to escalate, posing a serious threat to ecosystems and human health worldwide. It’s crucial to understand the scale of this problem and the need for comprehensive strategies to address the disposal and management of electronic waste.
Environmental Toxins Released by E-Waste
E-waste is not just an eyesore in landfills; it is a significant source of environmental toxins. Many electronic devices contain hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. When these materials are not properly disposed of and are left to decay in landfills, they can leach into soil and groundwater, contaminating ecosystems and posing health risks to animals and humans. The burning of e-waste, a common practice in some countries, releases toxic fumes that pollute the air and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
The dangers of these toxins cannot be overstated. Lead and mercury, for example, are neurotoxicants and can cause developmental issues and neurological damage in both wildlife and humans. Cadmium is a carcinogen and can lead to kidney failure. As e-waste continues to accumulate, the release of these toxins into our environment becomes more widespread, calling for urgent measures to prevent further contamination and protect public health.
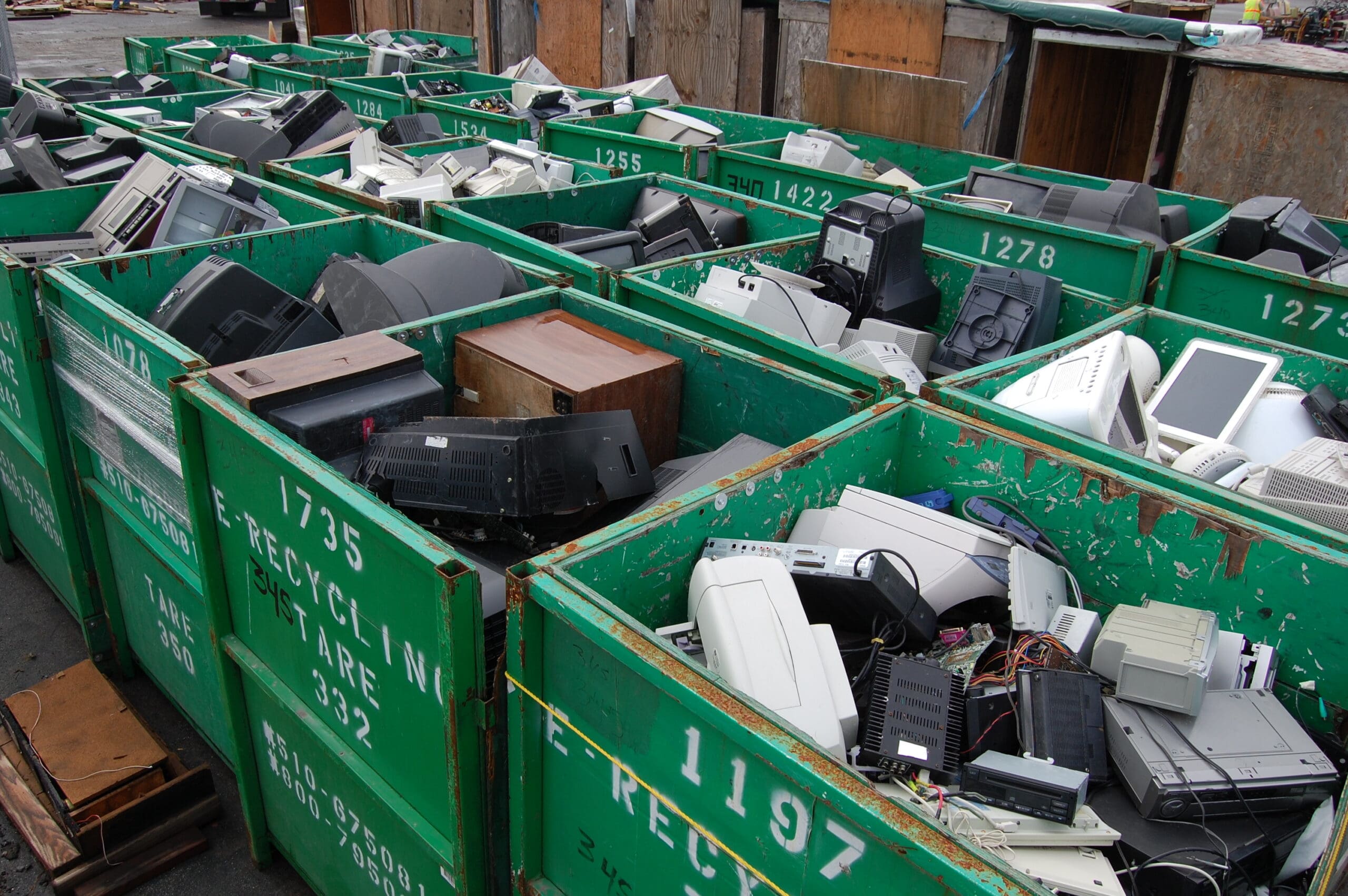

Global Inequities in E-Waste Management
The management of e-waste is riddled with global inequities. Developed nations often export a substantial portion of their electronic waste to developing countries, where regulations may be less stringent and recycling practices are often unregulated or informal. This transfer of e-waste places a disproportionate burden on the poorer regions of the world, where workers, including children, are exposed to toxic substances as they manually dismantle devices to recover valuable materials like gold and copper.
These practices not only result in environmental degradation in the host countries but also perpetuate a cycle of health risks and exploitation. The international community has recognized the need for more equitable and sustainable e-waste management solutions, including the enforcement of international agreements like the Basel Convention, which aims to control the transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and their disposal.

Innovative Solutions for E-Waste Reduction
The challenge of e-waste has sparked innovation and the development of various solutions aimed at reducing its impact. Technological advancements have led to the creation of more sustainable electronic products designed for easier disassembly and recycling. Companies are increasingly adopting extended producer responsibility (EPR) policies, which hold them accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life management.
On the consumer side, initiatives such as e-waste collection drives, buy-back programs, and recycling partnerships are gaining momentum. Moreover, there is a growing trend towards a circular economy, where products are designed to be reused, repaired, or recycled, thus minimizing waste. These solutions are crucial steps towards a sustainable future and require the collective effort of governments, businesses, and consumers to make a significant impact on e-waste reduction.
Taking Action: How Individuals Can Make a Difference
While e-waste is a global issue, individual actions can collectively make a substantial difference. Consumers can contribute by making more informed purchasing decisions, opting for electronics with a longer lifespan or those made from recycled materials. Proper disposal of electronics is also critical; individuals should take advantage of local e-waste recycling programs or donate functional devices for reuse.
Another powerful tool is advocacy. By raising awareness about the impacts of e-waste and demanding greater corporate responsibility, consumers can influence industry practices.
Additionally, supporting legislation that promotes sustainable production and responsible e-waste management can lead to systemic changes. The choices we make as individuals can drive progress towards a world where e-waste no longer poses a threat to our planet and its inhabitants.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future
The crisis of electronic waste presents a formidable challenge but also an opportunity for transformative action. As we have explored, the unseen consequences of e-waste affect our environment, health, and global equity. The release of toxins from improperly disposed electronics, the burden placed on developing nations, and the unsustainable production and consumption cycles are issues that require urgent and concerted efforts.
To mitigate these consequences, we must embrace a multifaceted approach. Governments need to enforce stricter regulations on e-waste management and ensure compliance with international agreements. Businesses must adopt sustainable practices and take responsibility for the lifecycle of their products through extended producer responsibility policies. Innovations in product design and recycling technologies can pave the way for more sustainable electronics.
Individuals play a critical role as well. By making informed purchasing choices, properly disposing of electronic devices, participating in recycling programs, and advocating for responsible corporate practices and legislation, each of us can contribute to reducing the impact of e-waste.
Collective action is essential. The path to a sustainable future lies in our ability to work together—governments, businesses, and individuals—to create systems that prioritize environmental health, equity, and sustainability. By addressing the e-waste crisis with urgency and innovation, we can protect our planet and ensure a healthier future for generations to come.
Unleash your impact potential today
Join our Community for the latest news, resources, and inspiring stories of entrepreneurial impact. Sign up now and ignite your journey towards making a difference.
You also might like

Are You Missing Critical IP Protections for Your Startup?
Are You Missing Critical IP Protections for Your Startup?

Footprints of Change: A Recap of the Climate Summit
Footprints of Change: A Recap of the Climate Summit


